III. RÉGLAGES DE BASE
3.1 - Paramétrer le système
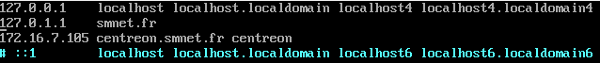
- Modifiez le fichier "/etc/hosts" de la manière suivante (IP pour notre Centreon : 172.16.7.105) :
Figure 1 - Fichier /etc/hosts
- Désactivez "IPv6" (Facultatif) :
#vi /etc/sysctl.d/disable-ipv6.confnet.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1#sysctl -p#vi /etc/netconfig# udp6 tpi_clts v inet6 udp - - (Ligne à commenter)# tcp6 tpi_cots_org v inet6 tcp - - (Ligne à commenter)#vi /etc/hosts# ::1 (Ligne à commenter)#vi /etc/ssh/sshd_configAddressFamily inet#vi /etc/sysconfig/chronydOPTIONS="-4"
- Effectuez une mise à jour du système :
#yum update#reboot
- Installez les utilitaires suivants :
#yum install vim net-tools bash-completion wget curl lsof bind-utils mailx git \redhat-lsb zip unzip
- Verrouillez le pavé numérique :
#vi /usr/local/bin/numlock#!/bin/bashINITTY=/dev/tty[1-6]for tty in $INITTY; dosetleds -D +num < $ttydone#chmod +x /usr/local/bin/numlock#chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local#echo "/usr/local/bin/numlock" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local#systemctl start rc-local#systemctl status rc-local
- Installez les outils de développement suivants :
#yum install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake libxml2-devel kernel-devel \kernel-headers-`uname -r`
3.2 - Paramétrer SNMP
SNMP signifie Simple Network Management Protocol. Il s'agit d'un protocole réseau qui permet de gérer les équipements d'un réseau et de diagnostiquer les problèmes du réseau.
#vi /etc/snmpd/snmpd.confagentAddress udp:161rocommunity publiccom2sec notConfigUser default publicsyslocation SMNetsyscontact centreon@smnet.fr#vi /etc/sysconfig/snmpdOPTIONS="-LS4d"#systemctl daemon-reload#systemctl restart snmpd
3.3 - Paramétrer MariaDB
Le paramétrage présenté ici est facultatif à l'exception des variables 'sql_mode' et 'open_files_limit'.
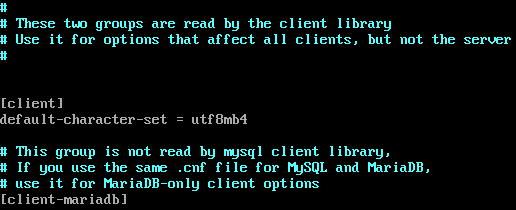
#vi /etc/my.cnf.d/client
Figure 1 - /etc/my.cnf.d/client.cnf
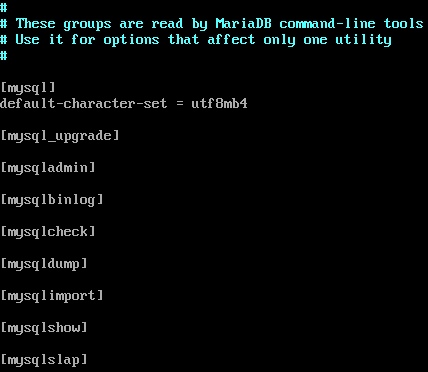
#vi /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-clients.cnf
Figure 2 - /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-clients.cnf
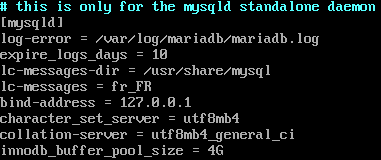
#vi /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
Figure 3 - /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
#mkdir /var/log/mariadb#chown mysql:mysql /var/log/mariadb#systemctl daemon-reload#systemctl restart mariadb#mysql -u root -p mysql[mysql]>select user,host,password,plugin from user;[mysql]>SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost'=PASSWORD('votre mot de passe');[mysql]>SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'centreon'=PASSWORD('votre mot de passe');[mysql]>SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'127.0.0.1'=PASSWORD('votre mot de passe');[mysql]>delete from user where password="";[mysql]>flush privileges;[mysql]>drop database test;[mysql]>show variables like 'sql_mode';
Figure 4 - 'sql_mode'
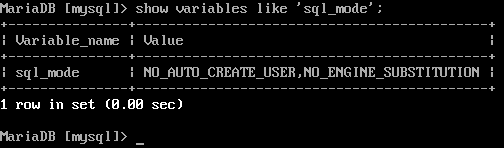
[mysql]>show global variables like 'open_files_limit';
Figure 5 - 'open_files_limit'
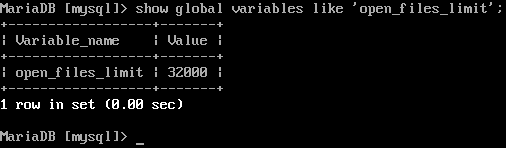
[mysql]>quit
3.4 - Paramétrer Php 7.2 et Httpd 2.4
- Modifiez les variables d'environnement pour Php 7.2 et Httpd 2.4 :
#scl enable rh-php72 bash#scl enable httpd24 bash
- Activez automatiquement Php 7.2 et Apache 2.4 au démarrage du système :
#which php#vi /etc/profile.d/rh-php72.sh
Figure 6 - rh-php72
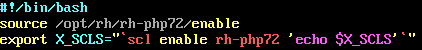
#which httpd#vi /etc/profile.d/httpd24.sh
Figure 7 - httpd24
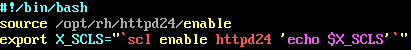
- Créez les liens suivants :
#ln -s /opt/rh/httpd24/root/etc/httpd/ /etc/#ln -s /opt/rh/httpd24/root/var/www/ /var/#ln -s /etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/php.ini /etc/#ln -s /etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/php-fpm.conf /etc/#ln -s /etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/pear.conf /etc/#ln -s /opt/rh/rh-php72/root/usr/bin/php /bin/#ln -s /opt/rh/httpd24/root/usr/sbin/httpd /sbin/
- Modifiez le fichier "/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf" :
#vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confLigne n° 86 :ServerAdmin centreon@smnet.frLigne n° 95 :ServerName centreon.smnet.frLigne n° 349 :ServerTokens ProdLigne n° 350 :KeepAlive onLigne n° 351 :RequestHeader unset Proxy early#systemctl restart httpd24-httpd
- Modifiez le fichier "/etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/php.ini" :
#vi /etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/php.iniLigne n° 197 :short_opoen_tag = OnLigne n° 374 :expose_php = OffLigne n° 404 :memory_limit = 128MLigne n° 672 :post_max_size = 128MLigne n° 691 :default_charset = "UTF-8"Ligne n° 825 :upload_max_filesize = 20MLigne n° 902 :date.timezone = Europe/Paris#cp /etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/php.ini \/opt/rh/rh-php72/register.content/etc/opt/rh/rh-php72/php.ini#systemctl restart httpd24-httpd
3.5 - Paramétrer Postfix
Si vous possédez un hébergement mutualisé chez OVH, vous pouvez utiliser un serveur de messagerie local et paramétrer OVH en "relayhost" pour envoyer des mails.
- Installez et paramétrez "Postfix" (Tenez compte de votre nom de domaine) :
#yum install postfix cyrus-sasl cyrus-sasl-plain mailx#vi /etc/hosts127.0.1.1 smnet.fr#mv /etc/postfix/main.cf /etc/postfix/main.cf.origin#cd /etc/postfix#grep -h -v '^[[:space:]]*\#' main.cf.origin | grep -v '^[[:space:]]*$' > main.cf#vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
Figure 8 - main.cf
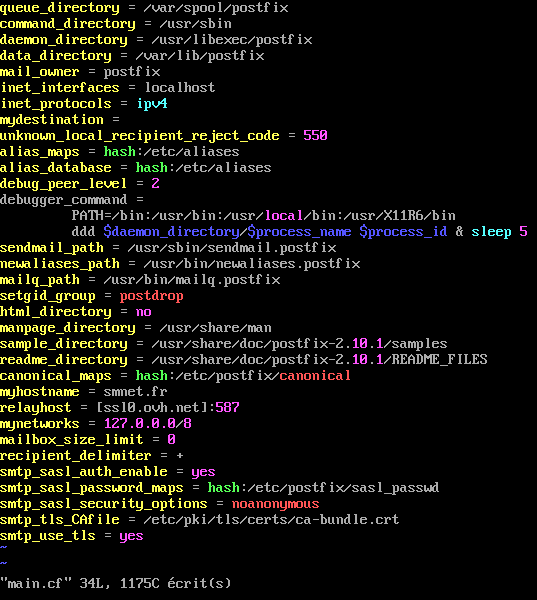
#vi /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd[ssl0.ovh.net]:587 centreon@smnet.fr:<mot de passe>#vi /etc/postfix/canonicalroot@smnet.fr centreon@smnet.frutilisateur@smnet.fr centreon@smnet.fr#postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd#postmap /etc/postfix/canonical#vi /etc/aliasesroot : centreon@smnet.fr#newaliases#systemctl start postfix#systemctl enable postfix
- Testez le fonctionnement de "Postfix" :
#echo "Test mail" | mail -s "Test Postfix sur Centreon" centreon@smnet.fr
- Vérifiez vos "logs" :
#cat /var/log/maillog
- Pour supprimer des mails dans la file d'attente :
#postsuper -d ALL